Bare Metal Forms and Helpers Walkthrough
09 May 2014Estimated time: 2-3 hours
Course: Ruby on Rails » Forms and Authentication » Project: Forms
##Objective
These projects will give you a chance to actually build some forms, both using nearly-pure HTML and then graduating to using the helper methods that Rails provides.
##Basic Steps:
First, create a basic Rails app with User Model and Controller.
From the command line, create a new Rails app:
jamies-air:~ jxberc$ rails new re-formerCreate and Migrate User Model:
jamies-air:re-former jxberc$ rails generate model User username:string email:string password:stringjamies-air:re-former jxberc$ db:migrateIn app/models/user.rb, add validations for presence:
class User < ActiveRecord::Base
validates :username, presence: true
validates :email, presence: true
validates :password, presence: true
endIn config/routes.rb, create routes for #new and #create actions:
ReFormer::Application.routes.draw do
resources :users, :only => [:new, :create]
endIn console, check to make sure routes were created:
jamies-air:re-former jxberc$ rake routes
Prefix Verb URI Pattern Controller#Action
user_index POST /user(.:format) user#create
new_user GET /user/new(.:format) user#new
jamies-air:re-former jxberc$Generate a UsersController:
jamies-air:re-former jxberc$ rails generate controller UsersIn app/controllers/users_controller.rb, write empty methods for #new and #create:
class UsersController < ApplicationController
def new
end
def create
end
endIn app/views/users folder, create new.html.erb file. Add boilerplate text to file.
From the command line, load development server using rails s. You should see the boilerplate text at ` http://localhost:3000/users/new`.
Build a form for creating a new user:
<form accept-charset="UTF-8" action="/users" method="post">
<label for="username">Username:</label>
<input id="username" name="username" type="text"><br>
<label for="email">e-mail:</label>
<input id="email" name="email" type="text"><br>
<label for="password">Password:</label>
<input id="password" name="password" type="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>If you try to submit data now you will receive an ActionController::InvalidAuthenticityToken error. Add authenticity token as follows:
<form accept-charset="UTF-8" action="/users" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="authenticity_token" value="<%= form_authenticity_token %>">
...Now if you try to submit data, you will get a template is missing error.
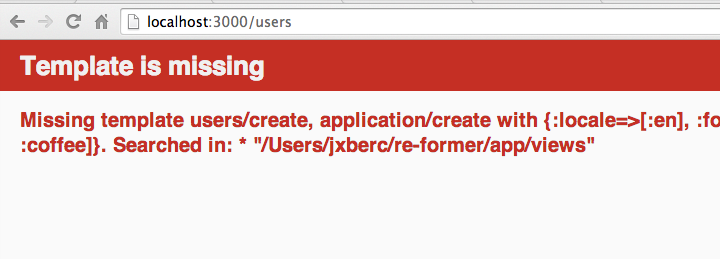
That is okay. This means we’ve reached our #create action in the controller and by default it looks for an app/views/users/create.html.erb file.
Instead, lets build the #create action to go elsewhere:
def create
@user = User.new(:username => params[:username], :email => params[:email], :password => params[:password])
if @user.save
redirect_to new_user_path
else
render :new
end
endIn app/controllers/users_controller.rb, create and implement a #user_params helper method:
class UsersController < ApplicationController
...
private
def user_params
params.require(:user).permit(:username, :email, :password)
endUpdate html form to submit hash of user parameters:
<form accept-charset="UTF-8" action="/users" method="post">
...
<input id="username" name="user[username]" type="text"><br>
...
<input id="email" name="user[email]" type="text"><br>
...
<input id="password" name="user[password]" type="password"><br>
...
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>Update #create action with new helper method:
class UsersController < ApplicationController
...
def create
@user = User.new(user_params)
if @user.save
redirect_to new_user_path
else
render :new
end
end
...Finally, confirm you can submit data using the form:
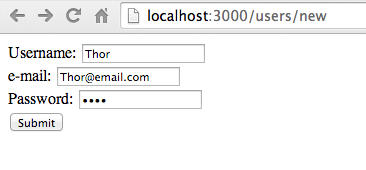
Log output:
Started POST "/users" for 127.0.0.1 at 2014-05-05 17:56:21 -0400
Processing by UsersController#create as HTML
Parameters: {"authenticity_token"=>"vapWanzKp+ZGIdvaE1HTcwS5ybQs/6pQJyuobJOcsmM=", "user"=>{"username"=>"thor", "email"=>"thor@email.com", "password"=>"[FILTERED]"}}
(0.1ms) begin transaction
SQL (0.4ms) INSERT INTO "users" ("created_at", "email", "password", "updated_at", "username") VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?) [["created_at", Mon, 05 May 2014 21:56:21 UTC +00:00], ["email", "thor@email.com"], ["password", "thor"], ["updated_at", Mon, 05 May 2014 21:56:21 UTC +00:00], ["username", "thor"]]
(0.6ms) commit transaction
Redirected to http://localhost:3000/users/new
Completed 302 Found in 14ms (ActiveRecord: 2.4ms)##Step 3: Build #form_tag Form
In this step, we will replace our html form with a #form_tag Form.
First, comment out your html form:
<!-- <form accept-charset="UTF-8" action="/users" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="authenticity_token" value="<%= form_authenticity_token %>">
<label for="username">Username:</label>
<input id="username" name="user[username]" type="text"><br>
<label for="email">e-mail:</label>
<input id="email" name="user[email]" type="text"><br>
<label for="password">Password:</label>
<input id="password" name="user[password]" type="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form> -->Switch to using #form_tag and #*_tag helper methods. Note that Rails will insert authenticity token automatically.
<%= form_tag("/users", method: "post") do %>
<%= label_tag(:username, "Username:") %>
<%= text_field_tag(:username) %><br>
<%= label_tag(:email, "email:") %>
<%= text_field_tag(:email) %><br>
<%= label_tag(:password, "password:") %>
<%= password_field_tag(:password) %><br>
<%= submit_tag("Submit") %>
<% end %>In app/controllers/user_controller.rb, modify#create method to once again accept normal top level User attributes.
def create
@user = User.new(:username => params[:username], :email => params[:email], :password => params[:password])
#@user = User.new(user_params)
...
endConfirm you can submit data.
##Step 4: Build #form_for Form
Modify your #new action in the controller to instantiate a blank User object and store it in an instance variable called @user.
class UsersController < ApplicationController
def new
@user = User.new
end
...Comment out #form_tag and build #form_for form:
<!-- <%= form_tag("/users", method: "post") do %>
<%= label_tag(:username, "Username:") %>
<%= text_field_tag(:username) %><br>
<%= label_tag(:email, "email:") %>
<%= text_field_tag(:email) %><br>
<%= label_tag(:password, "password:") %>
<%= password_field_tag(:password) %><br>
<%= submit_tag("Submit") %>
<% end %> --><%= form_for @user do |f| %>
<p>
<%= f.label :username %> <br/>
<%= f.text_field :username %>
</p>
<p>
<%= f.label :email %> <br/>
<%= f.text_field :email, :value => "example@email.com" %>
</p>
<p>
<%= f.label :password %> <br/>
<%= f.password_field :password %>
</p>
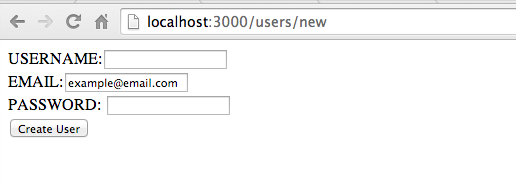
<p><%= f.submit %></p>Note: I’ve added a default placeholder value for :email.
Finally, in app/controllers/user_controller.rb, switch your controller’s #create method to accept the nested :user hash from params.
def create
#@user = User.new(:username => params[:username], :email => params[:email], :password => params[:password])
@user = User.new(user_params)
...
endConfirm you can submit data using the newly created #form_for form:
Update your routes and controller to handle editing an existing user.
In config/routes.rb:
ReFormer::Application.routes.draw do
resources :users, :only => [:new, :create, :edit, :update]
...In app/controllers/users_controller.rb:
class UsersController < ApplicationController
...
def edit
@user = User.find(params[:id])
end
def update
@user = User.find(params[:id])
if
@user.update(user_params)
redirect_to edit_user_path(@user)
else
render :edit
end
endCreate app/views/users/edit.html.erb. Copy/paste your form from the New view to Edit form:
<%= form_for @user do |f| %>
USERNAME:<%= f.text_field :username %> <br />
EMAIL:<%= f.text_field :email, :value => "example@email.com" %> <br />
PASSWORD: <%= f.password_field :password %><br />
<%= f.submit %>
<% end %>“View source” on the form generated by #form_for in your Edit view.
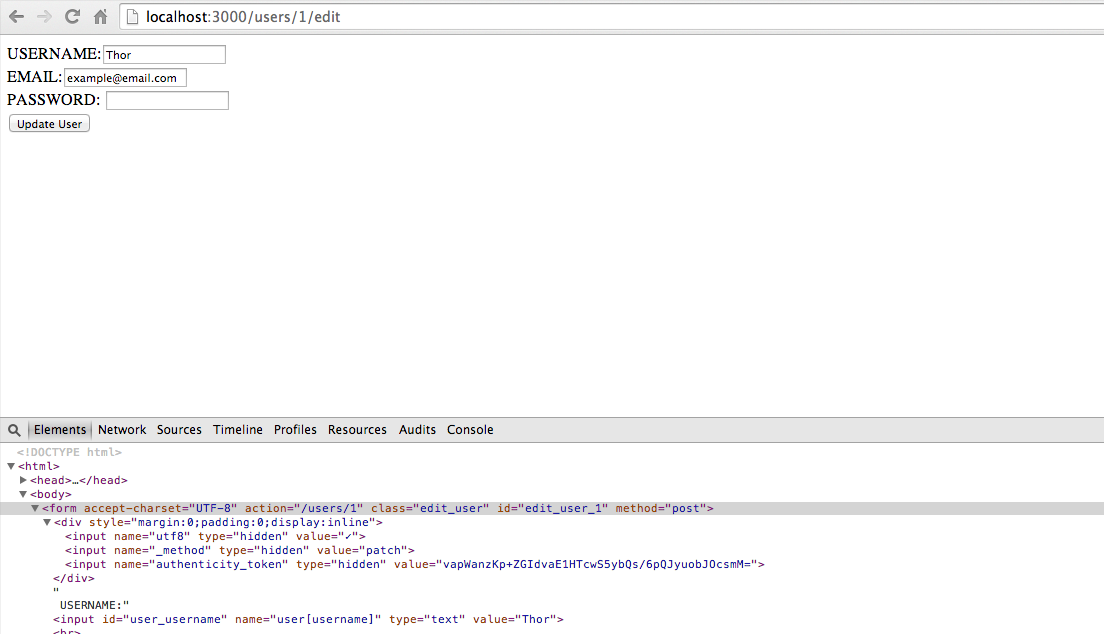
You should see authentication token and other relevant hidden fields.
Confirm that you can submit data and that validations are working.
In app/views/users/new.html.erb and app/views/users/edit.html.erb, include error messages:
<%= form_for @user do |f| %>
<ul>
<% @user.errors.full_messages.each do |error| %>
<li><%= error %></li>
<% end %>
</ul>
...Now, when validations fail, errors should display:
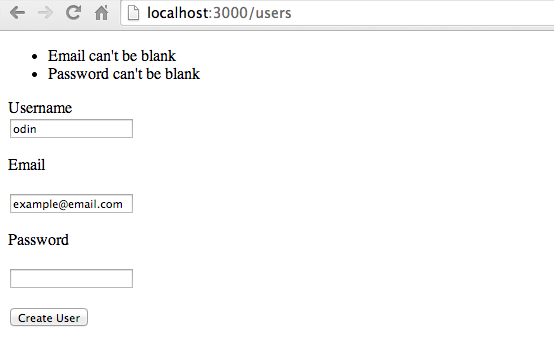
Congratulations! You’ve just created basic forms using html and ruby helper methods.